Are you unsure about antinutrients, where they are located, or are they dangerous for us? You will find the answer to all your questions in this article, so keep reading to explore more!
Antinutrients come in both artificial and natural categories, and they are mostly present in our foods, like grains, beans, legumes, and nuts. The task is to prevent the body from absorbing vitamins, nutrients, and minerals.
They may even block the digestive enzymes necessary for appropriate absorption. However, they exist in tiny amounts.
Usually, there are also benefits of antinutrients for our bodies rather than adverse effects. In addition, Antinutrients are also present in the roots of plants, leaves, and vegetables
and fruits.
Read on to explore why you should put efforts into antinutrients to get out of your diet immediately!
Good Antinutrients

The best thing? Firstly, not all antinutrients are harmful, and secondly, you may lessen the amount of the dangerous types.
It's not always clear which antinutrients are bad for our health. For example, polyphenols are a type that can be beneficial when they are consumed in fair amounts.
The same goes for flavonoids, another class of antinutrients that can be added to healthy meals and beverages like warm tea, cold coffee, and other whole plant foods.
On the other hand, beneficial antinutrients can also relatively block the absorption of minerals. But if you dont overconsume them, they are generally safe but even helpful.
Remember that even "good antinutrients" can stop the breakdown of enzymes, carbohydrates, proteins, copper, zinc, vitamin B1, and iron when consumed in extremely high amounts.
However, everyone responds differently to certain meals, so if you are responding badly after eating food, it is important to pay attention to your meal and, if necessary, consider changing it. How to Lower Your Body's Antinutrient Levels
Things You Need to Know About Antinutrients
Here is what you need to know about minimizing the amount of harmful antinutrients, or those that are more dangerous than helpful: Antinutrient-containing foods usually have much lower concentrations when sprouted.
Fermentation is the substance that can help incredibly healthy probiotic foods. The three simple methods for growing seeds—from grains, beans, nuts, or legumes—that make them easier to digest and permit your body to absorb their complete nutritional value are soaking, sprouting, and fermenting.
It is noticed that grains have less protein content, lack some essential amino acids, poorer protein and carbohydrate content, and the presence of certain antinutrients.
Antinutrient-rich foods should be germinated (or cooked for most vegetables), as this helps the absorption of multiple significant substances.
It also smooths digestion, lowers the risk of allergic reactions, and releases more vitamins, amino acids, and fiber from the seeds.
Even though soaking grains and other nutrient-blocking seeds won't totally rid them of all antinutrients, it's still a better option than consuming them unsoaked.
Avoid These Ten Antinutrients
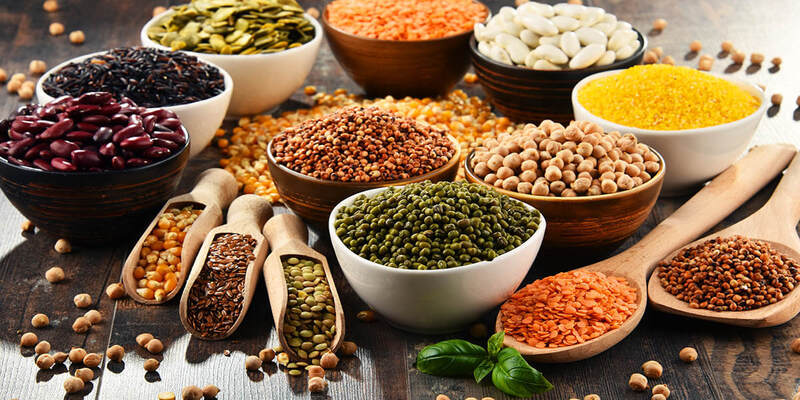

These ten antinutrients in your diet should be avoided as much as possible because they may cause deficiencies and upset stomachs.
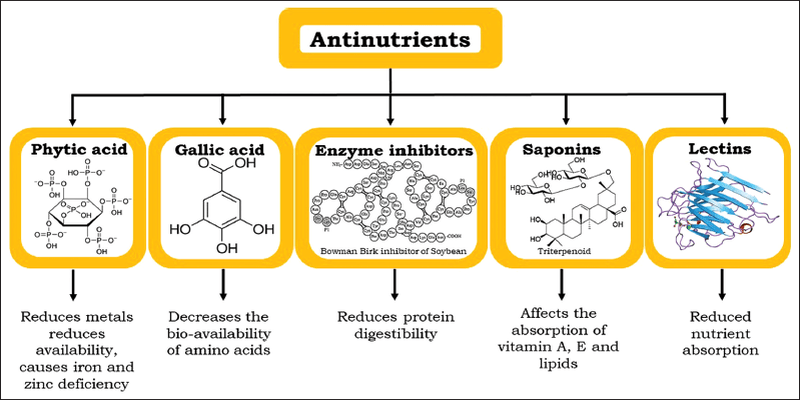
Phytate
Phytate is considered the most prominent antinutrient which prevents essential nutrients from being absorbed in the body However, some research has shown that phytate may prevent up to 80% of the phosphorous and zinc in foods like cashews and chickpeas and foods like pumpkin or sunflower seeds. It is also predicted that around 40% of foods are high in magnesium.
Oxalates
Oxalates are in very high concentrations in sesame seeds, black and brown millet, and soybeans. Based on multiple studies of edible plants for amino acids, these antinutrients provide plant proteins, specifically those from legumes, of "poor quality. Moreover, You can find excessive antinutrients in meat, which is not a good thing.
Gluten
Gluten is also an enzyme famous for gastrointestinal irritation production and is considered among the most challenging plant proteins to digest.
Moreover, gluten is also the main cause of multiple diseases, allergies, and cognitive issues. Moreover, celiac disease is a serious form of sensitivity to gluten. It is a genuinely allergic reaction to gluten. Often, people have minor symptoms, such as:
- Headache
- Memory loss
- Joint pain
- fatigue
Tannins
Tannins are another class of enzyme inhibitors that prevent proper digestion, which leads to gastrointestinal issues and even causes a shortage of protein.
However, molecules that contain enzymes can cause serious problems such as constipation, bloating, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal issues. We need enzymes to digest food and transport nutrients to our cells.
Lectins
As we discussed previously, lectins are mostly found in wheat and are the main cause of the lack of nutrients in the body. They may even lead to bloating and indigestion in many people. It also has the ability to cause harm to other parts of the body, like:
- loss of gut epithelial cells
- obstruct calcium absorption
- Digestion
- autoimmune reactions.
- rashes
- joint discomfort
- gastrointestinal distress
Soybeans, dairy products, and improperly prepared raw cereals all contain high quantities of lectin. But if you cook lectin-rich foods well, you can lower their lectin level without removing them from your diet.
You can almost eliminate lectins by cooking them thoroughly. The lectin concentration of grains and seeds can be reduced by soaking and sprouting them. Additionally, fermenting food can also help lower the lectin concentration.
Trypsin Inhibitors
Most grain-containing items, such as cereals, oatmeal, breads, and even baby meals, mainly include trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitors. Although heat processing and cooking usually break them down well, they can still cause issues like mineral deficiencies in young children, newborns, and people with impaired pancreatic function.
Saponins
Saponins also impact the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, which can lead to autoimmune diseases and other problematic syndromes. They can increase circulation and elicit immunological reactions, which are very difficult for us to digest.
Solanine
Solanine is generally found in nightshade foods such as tomatoes, peppers, and eggplant. These are often helpful antinutrients. However, it can result in "poisoning" with symptoms.
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- cramping in the stomach
- burning in the throat
- Headaches
- dizziness
Isoflavones
These specific polyphenolic antinutrients, primarily present in soybeans, may also cause changes in hormone levels and agitate digestive problems.
Aside from this, they are categorized as phytoestrogens, which are also called endocrine disruptors. These substances generally originate from plants that have estrogenic action and may cause unintentional changes in your hormone levels.
Chaconine
Let's talk about Chaconine. This molecule is ordinarily present in potatoes and other Solanaceae plants and is very helpful if you take it in moderate amounts because it has antifungal qualities.
However, in specific individuals, mainly when you consume it raw and in large quantities, it can cause stomach problems.
Conclusions
That's all there is to know about antioxidants. There are many antinutrients that can generate gastrointestinal inflammation and even cause problems in the digestion of food.
Not only this, but it can also raise the risk or severity of disease. Antinutrients are a high risk to you if you are sick and consuming an excessive amount of antinutrient-rich food.
So try to eat vegetables low in anti-nutrients. However, you can easily prevent this situation from happening. If you take these antinutrients in moderate amounts, this is limited to overindulgence in consumption.